The Art and Science of Demolition Techniques, Safety, and Environmental Impact
Demolition might seem like the chaotic counterpart to construction, but it’s an essential part of urban development and renewal. From clearing old buildings to making way for new infrastructure, destruction plays a crucial role in shaping our cities and communities.
Types of Demolition
Manual demolition involves breaking down structures by hand using tools like sledgehammers, pry bars, and jackhammers. This method is often used for smaller projects or delicate jobs where precision is key.
Mechanical Demolition
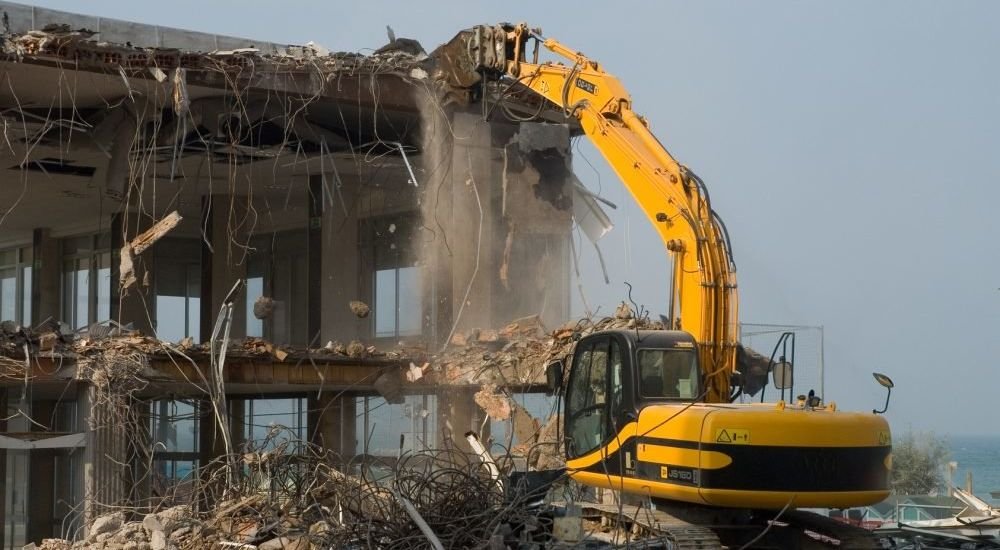
Mechanical destruction employs heavy construction machines such as excavators, bulldozers, and wrecking balls to dismantle buildings. Due to its efficiency and speed, it’s the go-to method for larger structures.
Implosion
Implosion is a highly specialized form of destruction that uses carefully placed explosives to collapse a building inward. It’s a dramatic and efficient way to bring down large structures in densely populated areas.
Site Assessment
Before any demolition, a thorough site assessment is crucial. This involves evaluating the building’s structure, identifying hazardous materials, and understanding the surrounding environment.
Legal Requirements
Demolition projects must comply with local regulations, which often require permits and adherence to safety standards. Failing to meet these requirements can lead to legal complications and fines.
Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount in destruction. This includes securing the site, using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and having emergency procedures in place.
Manual Destruction
Tools Used in Manual Destruction
Common tools include sledgehammers, pry bars, chisels, and jackhammers. These tools allow workers to carefully deconstruct parts of a building.
Step-by-Step Process
- Clear the area of non-structural elements.
- Begin deconstructing structural components from the top down.
- Carefully remove debris to minimize dust and hazards.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Greater control and precision, lower noise levels. Cons: Time-consuming, labor-intensive, and potentially more costly for large projects.
Mechanical Demolition
Equipment Used
Heavy machinery like excavators, bulldozers, wrecking balls, and cranes are staples of mechanical destruction. These machines can swiftly tear down large structures.
Techniques Involved
Techniques vary depending on the structure but often include top-down destruction and selective destruction, which targets specific parts of a building for removal.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Faster and more efficient for large buildings. Cons: Higher noise levels, more dust, and greater environmental impact if not managed properly.
How Implosion Works
Implosion involves placing explosives in key structural points of a building. When detonated, these explosives cause the building to collapse inward, minimizing the impact on surrounding areas.
Famous Implosion Projects
Notable implosions include the Seattle Kingdome and the Stardust Resort and Casino in Las Vegas. These projects demonstrated the precision and effectiveness of implosion in urban environments.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Quick, efficient, minimizes damage to nearby structures. Cons: Requires expert planning, potential for unexpected results, significant preparation time.
Environmental Considerations
Recycling Materials
Demolition can generate a large amount of waste, but much of it can be recycled. Metals, concrete, and wood are often repurposed, reducing the environmental impact.
Handling Hazardous Materials
Asbestos, lead paint, and other hazardous materials need careful handling. Specialized teams are often brought in to safely remove and dispose of these substances.
Minimizing Dust and Noise
Using water sprays to dampen dust and scheduling work during less disruptive times can help mitigate the environmental impact of demolition.
Safety Measures in Destruction
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers must wear appropriate PPE, including helmets, gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots, to protect against the numerous hazards on a destruction site.
Safety Protocols
Strict safety protocols should be followed, including regular site inspections, clear communication, and training for all personnel.
Emergency Procedures
Having a clear plan for emergencies, such as accidental collapses or injuries, is crucial. This includes first aid stations and quick access to medical services.
Economic Aspects of Demolition
Cost Factors
The cost of demolition depends on the size of the project, the methods used, and the disposal of materials. Budgeting accurately is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.
Budgeting for Demolition Projects
A detailed budget should include costs for permits, labor, machinery, and waste disposal. Contingency funds are also important for unforeseen issues.
Economic Impact on Communities
Destruction can have significant economic impacts, such as job creation during the project and potential boosts in property values post-demolition.
Technological Advances in Demolition
Robotics are increasingly used for precision tasks and in hazardous environments, reducing the risk to human workers and increasing efficiency. Modern machinery with improved capabilities can handle larger and more complex demolition tasks, making projects faster and safer.
Future Trends
Innovations such as AI-driven machinery and more sustainable demolition practices are on the horizon, promising to transform the industry further.
Case Studies
Successful Demolition Projects
Projects like the demolition of the Tappan Zee Bridge highlight the importance of planning, safety, and community involvement in successful demolitions.
Lessons Learned from Failed Demolitions
Failed demolitions, such as the incomplete collapse of the Ocean Tower in Texas, provide valuable lessons in the importance of thorough planning and risk assessment.
Regulations and Compliance
Compliance with local and international standards ensures that demolitions are carried out safely and legally. These standards cover everything from environmental impact to worker safety. Obtaining the necessary permits and passing inspections are critical steps in any destruction project. These processes help ensure that the project meets all regulatory requirements. Failure to comply with regulations can lead to legal action, fines, and delays. It is essential to stay informed about the relevant laws and regulations.
Challenges in Demolition
Dealing with Unforeseen Issues
Unexpected issues such as hidden hazardous materials or structural instabilities can arise, requiring quick and effective solutions. Demolishing complex structures, especially those with historical significance or unusual designs, can present unique challenges.
Community Concerns
Addressing the concerns of the local community, such as noise, dust, and safety, is vital to ensure smooth project execution and maintain good relations.
The Future of Destruction
Innovations on the Horizon
Emerging technologies like drones for site inspections and 3D modeling for planning are set to revolutionize demolition practices.
Sustainability in Destruction Practices
Sustainable practices, including greater emphasis on recycling and reducing environmental impact, are becoming increasingly important in the industry.
Predictions for the Industry
The destruction industry is poised for significant advancements, with a focus on safety, efficiency, and sustainability driving future developments.
Conclusion
Demolition is more than just knocking down buildings; it’s a complex and essential part of urban development. By understanding the various methods, safety protocols, and environmental considerations, we can appreciate the vital role destruction plays in shaping our world. Safe and efficient destruction practices are crucial for creating spaces for new developments while minimizing negative impacts on communities and the environment.
If you gained new insights from this article, explore our blog, Gimkit, for more enlightening content.













Post Comment